Imaginary Number
The regular numbers you usually work with are from the Real Number System. But, there is another kind of number - an imaginary number. Imaginary numbers are in the form:

For more info on imaginary numbers, check out my lessons on complex numbers. |
|

|
Improper Fraction
There's really nothing "improper" about them and we use them in algebra and higher math all the time. An improper fraction is when the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
For more info on improper fractions and how to change them into mixed numbers, check out my lesson onimproper fractions. |

|
|
|

|
Inequality
An inequality is like an equation, but without the "equals" sign. Instead, it has one of these signs:

Examples: 5 > 3 2x + 7 < -9 |
|

|
Infinite
An infinite list of numbers goes on forever and ever and never stops.
Example: The whole numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ... |
|

|
Infinity
Here is the official symbol for infinity... It's a "figure eight" laying on its side.
 |
|

|
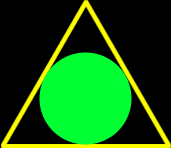
Inscribed
Example: The picture on the right... The circle is said to be inscribed in the triangle since the circle is inside so that its edge (circumference) is just touching each of the sides of the triangle. |
 |
|
|

|
Integer
An integer is one member of this set: { ... , -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... } |
|

|
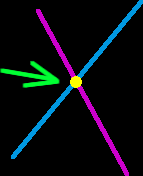
Intersection
An intersection is the place where two things cross. |
 |
|
|

|
Intersection of Sets
The intersection of two sets is a set of elements that appears in both sets.
Example: A = { 1, 2, 3, a, b, c } B = { 3, 4, 5, b, c, f, g }
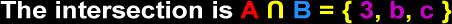 |
|

|
Inverse - Additive Inverse
The additive inverse of a number, a, is the number, -a, you add to it to get 0 (the additive identity).
a + (-a) = 0
Examples: The additive inverse of 8 is -8 since 8 + (-8) = 0
The additive inverse of -2 is 2 since -2 + 2 = 0 |
|

|
Inverse - Multiplicative Inverse
The multiplicative inverse of a number, a, is the number, 1/a, that you multiply it to so you get 1 (the multiplicative identity).

Example: The multiplicative inverse of 5 is 1/5.
The multiplicative inverse of 1/2 is 2. |
|

|
Irrational Number
An irrational number is a number whose decimal part goes on forever and ever without repeating.
 |
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|