|
|
|

|
Percent
Percents are like fractions and decimals because they count PART of something. Whole numbers (0, 1, 2, 3, ...) count whole things -- like a whole pizza. You can use a percentages to count part of the pizza. Half of a pizza would be 50% of a pizza. One-fourth of a pizza would be 25% of a pizza.
Examples: 20% 0.05% 245.2%
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
Permutations
A permutation is an arrangement of objects.
Example: How many ways can you arrange the letters A, B and C? 6 ways
ABC ACB BAC BCA CAB CBA
For more info, check out my Permutations lesson. |
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
Point
A point is a location in space. I can't even draw you a real picture of a point, because my dot would really be a blob of points. It's impossible to really draw just one point. So, when you're in Algebra and you have to graph points, you'll just have to pretend. |
|

|
|
|
|

|
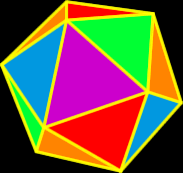
Polyhedron
A polyhedron is a three-dimensional object whose faces are polygons. The most famous set of polyhedra (that's the plural) is the five Platonic Solids that may have been discovered by Pythagoras. These solids are special because they are the only ones that are made up of regular polygons. They are the tetrahedron, the cube (hexahedron), the octahedron, the dodecahedron and the icosahedron.
For more info, check out my Polyhedra Gallery. |
|
|
|

|
Polynomial
For now (and probably forever), you can just think of a polynomial as a bunch of blobs that are being added and subtracted. The blobs are just products of numbers and variables (letters) with exponents. Here's an example:
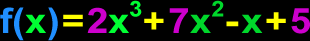
For more info and more examples, check out my Polynomial lessons. |
|

|
Positive Numbers
Positive numbers are those that appear to the right of zero on the number line.
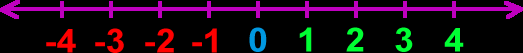 |
|

|
Prime
A number is prime if it has exactly two factors: 1 and itself. The number 20 is not a prime number since it has more than two factors: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20. The number 20 is composite. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite since it only has one factor: 1.
Here are some prime numbers: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, ... |
|

|
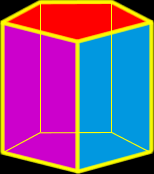
Prism
A prism is a polyhedron that is formed with two parallel polygons (the bases - top and bottom)that are connected at the edges with rectangles. My example in the picture is a right prism since the sides form right (90 degree) angles with the bases. |
|
|
|

|
Probability
A probability tells us how likely it is for an event to occur. When the weatherman says there's a 60% chance of rain, that's a probability. When you toss a coin, there's a 50% (1/2) probability that "tails" will come up.
Let's look at rolling a die... There are 6 possible rolls (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). This number goes in the denominator. What if we want to know the probability for rolling a 5... There is one 5 on a die... So, there's one chance out of six that we'll roll a 5. That's a 1/6 probability. What if we want to roll an odd number? There are three odd numbers on a die (1, 3, 5)... That's three chances out of six... That's a 3/6 (or 1/2) probability. |
|

|
Product
The product is the answer when you multiply two (or more) numbers.
Example: 3 x 2 = 6
For more info, check out my Multiplication Lessons. |
|

|
Proof
A proof is an argument that shows something (like a theorem) is true beyond any doubt. In math, sometimes a proof is all numbers and symbols and sometimes there are sentences too.
There are different kinds of formal proofs in math: direct proof, indirect proof and mathematical induction, to name a few. |
|

|
|
|
|

|
Proportion
A proportion is simply two ratios that are equivalent to each other. Proportions are usually used in Algebra to solve for some missing information. |
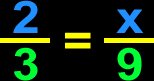
|
|
|

|
Protractor
A protractor is a device used in Geometry to measure and draw angles. |
|

|
|
|
|

|
Pythagorean Identities
The Pythagorean Identities are

For more info on the Pythagorean Identities and where they come from, check out my Pythagorean Identities lesson. |
|

|
|
|
|

|
Pythagorean Triples
Pythagorean triples are also called Pythagorean numbers. These are whole numbers that work together in the Pythagorean theorem.
 
|